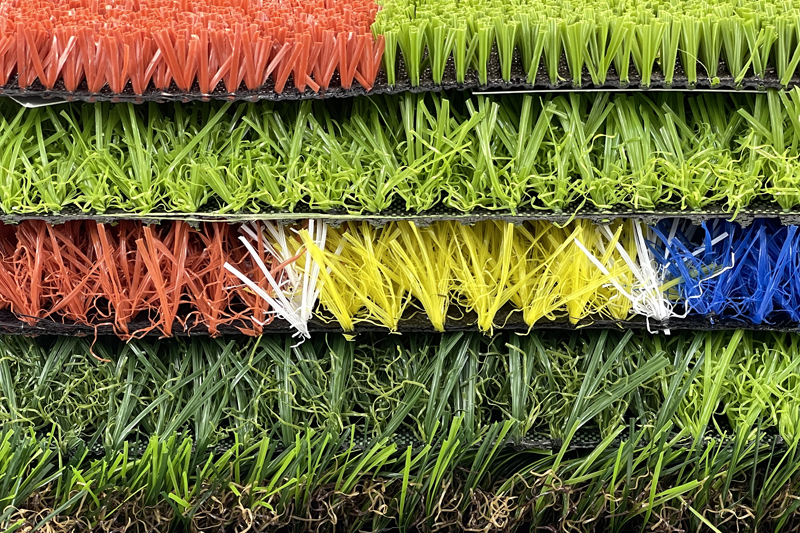
The raw materials of artificial turf are mainly polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride and polyamide can also be used. The leaves are painted green to imitate natural grass, and ultraviolet absorbers need to be added. Polyethylene (PE): It feels softer, and its appearance and sports performance are closer to natural grass, which is widely accepted by users. It is the most widely used raw material for artificial grass fiber on the market. Polypropylene (PP): The grass fiber is harder, generally suitable for tennis courts, playgrounds, runways or decorations. The wear resistance is slightly worse than polyethylene. Nylon: It is the earliest raw material for artificial grass fiber and belongs to the generation of artificial grass fiber.
Material structure Artificial turf consists of 3 layers of materials. The base layer is composed of compacted soil layer, gravel layer and asphalt or concrete layer. The base layer is required to be solid, non-deformed, smooth and impermeable, that is, a general concrete field. Due to the large area of the hockey field, the base layer must be handled well during construction to prevent sinking. If a concrete layer is laid, expansion joints must be cut after the concrete is cured to prevent thermal expansion deformation and cracks. Above the base layer is a buffer layer, usually made of rubber or foam plastic. Rubber has moderate elasticity and a thickness of 3~5mm. Foam plastic is less expensive, but has poor elasticity and a thickness of 5~10mm. If it is too thick, the lawn will be too soft and easy to sag; if it is too thin, it will lack elasticity and will not play a buffering role. The buffer layer must be firmly attached to the base layer, usually with white latex or glue. The third layer, which is also the surface layer, is the turf layer. According to the surface shape of the manufacturing, there are fluff turf, circular curly nylon turf, leaf-shaped polypropylene fiber turf, and permeable turf woven with nylon filaments. This layer must also be glued to the rubber or foam plastic with latex. During construction, the glue must be fully applied, pressed tightly in turn, and no wrinkles can be formed. Abroad, there are two common types of turf layers: 1. The leaf-shaped fibers of the turf layer are thinner, only 1.2~1.5mm; 2. The turf fibers are thicker, 20~24mm, and quartz is filled on it almost to the top of the fiber.
Environmental protection
Polyethylene, the main component of artificial turf, is a non-biodegradable material. After 8 to 10 years of aging and elimination, it forms tons of polymer waste. In foreign countries, it is generally recycled and degraded by companies, and then recycled and reused. In China, it can be used as a foundation filler for road engineering. If the site is changed to other uses, the base layer built by asphalt or concrete must be removed.
Advantages
Artificial turf has the advantages of bright appearance, green all year round, vivid, good drainage performance, long service life, and low maintenance cost.
Problems during construction:
1. The marking size is not accurate enough, and the white grass is not straight.
2. The strength of the joint belt is not enough or the lawn glue is not used, and the lawn turns up.
3. The joint line of the site is obvious,
4. The direction of the grass silk lodging is not regularly arranged, and the light reflection color difference occurs.
5. The surface of the site is uneven due to uneven sand injection and rubber particles or the lawn wrinkles have not been processed in advance.
6. The site has odor or discoloration, which is mostly due to the quality of the filler.
The above problems that are prone to occur during the construction process can be avoided as long as a little attention is paid and the artificial turf construction procedures are strictly followed.
Post time: Jul-10-2024